What Are On-Page SEO Elements and How Do They Work
On-page SEO elements are parts of a webpage you can improve. These help search engines and people understand your content better. For example, Google changes over 61% of title tags. This happens because of problems like being too long or repeating words. Fixing these parts makes your site rank higher and attract more users.
Key Takeaways
On-page SEO parts like title tags and meta descriptions help search engines understand your site. Fixing these can boost your site's rank.
Use keywords smartly in titles and text. This helps people find your content and makes it match what they search for.
Simple URL structures make it easier for users and search engines. Keep URLs short and add keywords to them.
Linking pages on your site helps users move around easily. It also helps search engines find your pages faster.
Optimizing images makes your site load quicker and look better. Add alt text and shrink image sizes to speed up loading.
Key On-Page SEO Elements
On-page SEO elements are key to making your website easier to find. These parts help search engines understand your site and guide users to useful content. Let’s look at three main parts: title tags, meta descriptions, and using keywords in content.
Title Tag
The title tag is a very important on-page SEO element. It shows as the clickable link in search results. A good title tag can boost your ranking and attract more visitors.
Put main keywords at the start for better results.
Make titles interesting and include keywords naturally.
Match the title tag with the H1 header for consistency.
Don’t overuse keywords, as it can hurt your SEO.
For example, if your page is about "Healthy Recipes," a good title tag could be: "Healthy Recipes for Quick and Easy Meals | YourBrand." This uses the main keyword, adds value, and includes your brand name.
Meta Descriptions
A meta description is a short summary of your page that shows under the title tag in search results. It doesn’t directly affect rankings but helps get more clicks.
Write catchy meta descriptions with important keywords.
Use action words to make people want to click.
Add the exact search term to match what users want.
Keep it between 140-155 characters to avoid cutting off.
Show unique features or facts to stand out.
For example, a meta description for "Healthy Recipes" could be: "Discover quick and easy healthy recipes for your busy life. Try our tasty meals today!" It’s short, engaging, and uses the right keywords.
Keywords and Content Optimization
Keywords are the heart of on-page SEO. They tell search engines what your content is about. Good content optimization means using keywords smartly while keeping it easy to read.
Add keywords to headings, subheadings, and main text.
Use one H1 header and organize with H2s and H3s.
Write helpful content that answers user questions.
Update metadata with main keywords to rank higher.
Don’t overuse keywords, or you might get penalized.
For example, if your keyword is "healthy recipes," use it in the H1 header, subheadings like "Quick Healthy Recipes," and naturally in the text. Adding images with descriptive alt text can also improve your SEO.
Tip: Focus on creating great content, not just adding keywords. Search engines prefer quality content that helps users.
URL Structure
A good URL structure helps search engines and users. Search engines use URLs to understand pages, and users use them to navigate. Making URLs SEO-friendly improves visibility and user experience.
Add keywords to URLs to explain the page topic. For example, a blog about "Healthy Recipes" could use
www.yourbrand.com/healthy-recipes.Use hyphens to separate words. Avoid underscores or spaces, as they confuse search engines.
Keep URLs short and easy to read. Long URLs can be hard to follow and reduce clicks.
Always use lowercase letters. This avoids problems and keeps your site consistent.
For big websites, organize URLs in a clear structure. This helps users and search engines find content easily.
Use HTTPS for security and to gain visitors' trust.
A 2023 study showed that pages with keyword-matching URLs got more clicks. This proves that clear and short URLs help users and improve SEO.
Internal Linking
Internal links connect pages on your site. They help users and search engines find content. This improves navigation, indexing, and user experience.
Example of Internal Linking Change | Result |
|---|---|
Adding Links to Nearby Locations | |
Linking Related Articles | Helped main pages, mixed results for others. |
Fixing Redirect Links | Better crawling and user experience. |
Reducing Too Many Links in One Spot | Higher rankings for linked pages. |
Adding Links in Homepage Footer | 5% more traffic to key pages. |
To improve internal linking:
Link to related pages with clear anchor text. This helps users and search engines understand the link.
Don’t add too many links on one page. Focus on useful links to keep it simple.
Update old pages with links to new ones. This keeps your site fresh and connected.
Place links to important pages in visible spots, like the homepage footer.
Good internal linking makes your site stronger and helps users find what they need.
Image Optimization
Images make your content better but can slow your site. Optimizing images makes your site faster and improves SEO.
Compress images to make them smaller without losing quality. For example, Swimply reduced image size by 38%, making their site 50% faster.
Add alt text to describe images. This helps search engines and visually impaired users.
Pick the right file type, like JPEG, PNG, or WebP. WebP often works best for quality and size.
Use responsive images so they look good on all devices. Culture Kings made images load in 13 milliseconds, improving mobile use.
Use caching to load images faster. BentoBox reached a 100% cache hit rate, speeding up their site.
Optimizing images makes your site faster and keeps users happy. For example, Judge.me cut load time to 100 milliseconds, which increased conversions.
Schema Markup
Schema markup helps search engines understand your webpage better. It is structured data added to your page's HTML. This data gives extra details about your content. It helps search engines show rich and detailed search results.
Using schema markup makes your page stand out. For example, a product page can show price, stock, and reviews in search results. This makes your page more noticeable and gets more clicks.
Here are some benefits of schema markup:
It improves search visibility with rich snippets like ratings or images.
It helps search engines create features like knowledge panels or carousels.
It shows users helpful details quickly, like event times or prices.
Adding schema markup boosts your SEO strategy. Even if your rank is lower, rich snippets can attract more visitors. For example, a recipe blog can show cooking time, ingredients, and ratings in search results. These details help users choose your page.
To add schema markup, use tools like Google's Structured Data Markup Helper. This tool helps you tag your content correctly. After adding it, test it with Google's Rich Results Test to ensure it works.
Schema markup makes your content easier for search engines and users to understand. This small change can greatly improve your site's visibility and performance.
Why On-Page SEO Elements Matter
Boosting Search Engine Rankings
On-page SEO helps your site rank higher in searches. Search engines check these elements to see if your content fits a user’s question. Fixing title tags, meta descriptions, and keywords makes your page clearer to search engines. This improves your chances of showing up in top results.
For example, placing keywords smartly in your text and metadata helps match user searches. A simple URL and good internal links also help search engines find and organize your site. These steps improve your ranking and bring more visitors to your page.
Making User Experience Better
On-page SEO isn’t just for search engines; it helps users too. When your site is easy to read and navigate, people stay longer. Things like headings, bullet points, and clear images make your content more enjoyable.
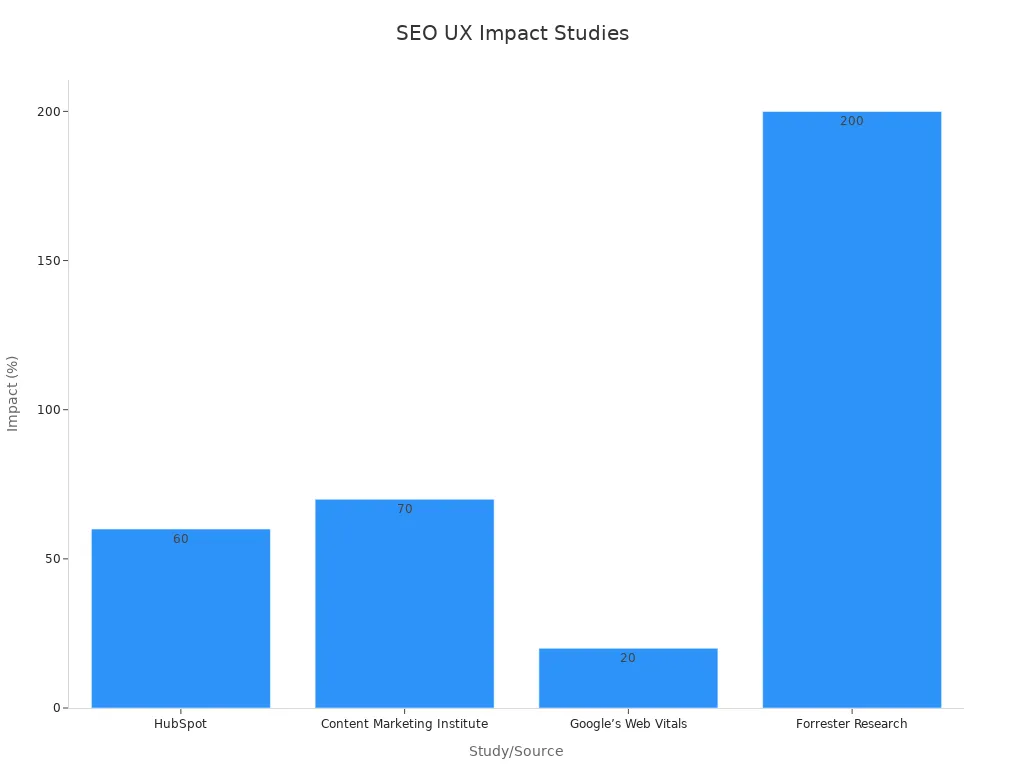
Here’s a table showing how on-page SEO improves user experience:
Study/Source | Finding | Impact |
|---|---|---|
HubSpot | 60% of users like content with headings, bullet points, and images. | Makes users trust your site and enjoy it more. |
Content Marketing Institute | Good content and design can increase time spent on a page by 70%. | Shows Google your content is helpful. |
Google’s Web Vitals | Faster load times can boost conversions by 20%. | Keeps users engaged and improves sales. |
Forrester Research | Better design can raise conversion rates by 200%. | Users see your site as reliable and useful. |
Moz | Sites with good engagement often rank higher. | Proves that user-friendly sites help SEO. |
Focusing on user experience keeps visitors on your site longer. It also tells search engines your content is valuable. This benefits both your users and your SEO.
Helping Bigger SEO Plans
On-page SEO is the base of a strong SEO plan. It works with off-page and technical SEO to make your site better. For example, using keywords and linking pages helps match what users search for. This supports other SEO efforts and improves your site’s performance.
Good on-page SEO also builds your site’s trust. Search engines rank user-friendly and helpful content higher. This boosts your site’s visibility and strengthens your overall SEO. By improving on-page elements, you set up your site for long-term success.
Easy Steps to Improve On-Page SEO Elements
Making Great Title Tags
A title tag is the first thing people see. It’s the clickable headline in search results. A good title tag helps your page stand out.
Put your main keyword at the start of the title. This helps search engines know your topic and rank you higher.
Use words like "best tips" or "easy guide" to grab attention. These make people curious and want to click.
Turn your title into a question if it fits. Questions like "What Are the Best SEO Tips?" make users want answers.
Keep it short, under 55 characters, so it shows fully on all devices.
Add your brand name at the end for trust and recognition.
For example, a title for an SEO blog could be: "SEO Tips for Beginners: Rank Higher Today | YourBrand." This title uses the keyword, is interesting, and includes the brand name.
Studies show that good title tags bring more clicks. This means more people visit your site. By writing clear and catchy titles, you can get better results.
Writing Catchy Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are short summaries under the title in search results. They don’t directly affect rankings but help get more clicks.
Write short, interesting summaries that show why your page is helpful.
Add keywords naturally to match what people search for.
Use action words like "Find," "Learn," or "Try" to make people click.
Keep it between 140-155 characters so it doesn’t get cut off.
Highlight special features or benefits to stand out from others.
For example, a meta description for SEO tools could be: "Find the best SEO tools to boost your site today. Start improving now!" It’s short, uses keywords, and encourages action.
Good meta descriptions make your page more noticeable. When more people click, search engines see your page as useful, which can help rankings.
Using Keywords Smartly
Keywords are the main part of on-page SEO. They connect your page to what people search for. Using them well helps your page rank higher.
Put your main keyword in the H1 header, subheadings, and first paragraph. This shows search engines your topic.
Use keywords naturally in your writing. Don’t overuse them, or it can hurt your ranking.
Write helpful content that answers what users want to know. Search engines like pages that give value.
Add keywords to title tags, meta descriptions, and image alt text for better results.
Use keywords in your URL to make it clear and easy to find.
For example, if your keyword is "SEO tips," use it in headings like "Best SEO Tips for Beginners" and in the text naturally. A good URL could be www.yourbrand.com/seo-tips.
Research shows that helpful content with the right keywords ranks better. By placing keywords smartly, you make your page easier to find and more useful for users.
Structuring URLs for SEO
A good URL structure helps search engines and users understand your page. It also makes your website easier to find and navigate. Follow these simple steps to create better URLs:
Use Keywords in URLs: Add your main keyword to the URL. This makes it clear and relevant. For example, if your page is about "SEO tips," use
www.yourbrand.com/seo-tips.Keep URLs Short and Simple: Avoid long, confusing URLs. Short ones are easier to read and share. For instance,
www.yourbrand.com/blog/seo-guideis better thanwww.yourbrand.com/blog/2023/10/seo-guide-for-beginners.Use Hyphens to Separate Words: Hyphens make URLs easier to read. Don’t use underscores or spaces, as they can cause problems.
Stick to Lowercase Letters: Always use lowercase letters in URLs. Uppercase letters can lead to errors and inconsistency.
Organize URLs Logically: For big websites, group similar pages under categories. For example, a clothing store could use
www.yourbrand.com/men/shirtsandwww.yourbrand.com/women/dresses.
Tip: Use HTTPS for your site. It keeps your site secure and builds trust with visitors.
Clear and simple URLs improve user experience and help search engines index your pages better.
Developing an Internal Linking Strategy
Internal links connect pages on your site. They help users find related content and guide search engines through your site. A good internal linking plan can boost your SEO and keep visitors interested.
Here’s how to create a strong internal linking strategy:
Link to Relevant Pages: Add links to pages that give more helpful information. For example, if you mention "SEO tips," link to a detailed guide about it.
Use Descriptive Anchor Text: The clickable text should explain where the link goes. Instead of "Click here," use "Learn more about SEO strategies."
Prioritize Important Pages: Link often to your most valuable pages, like product pages or key articles. This shows search engines these pages are important.
Avoid Overloading Links: Don’t add too many links on one page. Too many links can confuse users. Focus on quality links instead.
Update Old Content: Check older pages and add links to newer, related content. This keeps your site fresh and connected.
Note: Internal links improve navigation and help linked pages rank higher. It’s an easy way to make your site better.
Optimizing Images for SEO
Images make your content more interesting but can slow down your site if not optimized. Fixing images improves speed, user experience, and SEO.
Here are simple ways to optimize images:
Compress Images: Make image files smaller without losing quality. This speeds up your site.
Use Next-Gen Formats: Formats like WebP are smaller and better than JPEG or PNG.
Implement Lazy Loading: Load images only when users scroll to them. This makes pages load faster.
Resize Images: Make sure images fit the screen size. Large images can slow down your site.
Add Alt Text: Write short descriptions for images. This helps search engines and visually impaired users understand them.
Technique | How It Helps |
|---|---|
Image Compression | Makes files smaller, speeding up load times |
Next-Gen Formats | Keeps quality while reducing file size |
Lazy Loading | Loads images only when needed, improving speed |
Resizing Images | Fits images to screen size, making pages faster |
Tip: Use caching to save images temporarily. This helps returning visitors load pages faster.
Optimizing images makes your site faster and more user-friendly. This keeps visitors happy and shows search engines your site is high-quality.
Adding Schema Markup
Schema markup helps search engines understand your page better. It adds special data to your site, making it easier to show detailed search results. These results can include extra details like prices, ratings, or dates, which make your page stand out.
What Is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is a type of code added to your webpage. It explains your content in a clear, organized way for search engines. For example, if your page is about a recipe, schema markup can show cooking time, ingredients, and ratings. This information appears in search results, giving users a quick idea of your page.
Why Use Schema Markup?
Schema markup makes your page more visible and appealing in search results. Here are some benefits:
Better Visibility: Rich results like star ratings or prices grab attention.
Improved User Experience: Users see helpful details quickly, making your page more useful.
Higher Click Rates: Pages with rich snippets often get more visitors.
Steps to Add Schema Markup
Adding schema markup is simpler than it sounds. Follow these steps:
Pick the Right Schema Type: Visit schema.org to find the best type for your content, like recipes or events.
Use Google’s Markup Helper: This free tool helps you create schema markup. Highlight your content and assign tags.
Generate the Code: The tool will create the schema code for you.
Add the Code to Your Page: Copy the code into your page’s HTML, usually in the
<head>section.Test Your Code: Use Google’s Rich Results Test to check for errors before publishing.
Example of Schema Markup Code
Here’s an example of schema markup for a recipe:
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Recipe",
"name": "Chocolate Chip Cookies",
"author": "Jane Doe",
"datePublished": "2023-10-01",
"description": "A simple recipe for delicious chocolate chip cookies.",
"prepTime": "PT15M",
"cookTime": "PT10M",
"totalTime": "PT25M",
"recipeYield": "24 cookies",
"recipeIngredient": [
"2 cups flour",
"1 cup sugar",
"1 cup chocolate chips"
],
"recipeInstructions": [
"Preheat oven to 350°F.",
"Mix all ingredients in a bowl.",
"Scoop dough onto a baking sheet and bake for 10 minutes."
]
}
</script>
This code tells search engines key details about the recipe, like ingredients and cooking time.
Tip: Start with one page to practice adding schema markup. Once you’re confident, add it to more pages.
Best Practices for Schema Markup
Follow these tips to use schema markup effectively:
Stay Relevant: Use schema types that match your content.
Keep It Updated: If your content changes, update the schema too.
Don’t Overdo It: Only include important details in your markup.
Validate Your Code: Always test your schema to ensure it works.
Schema markup is a great way to improve your SEO. It helps search engines understand your content and increases your chances of showing rich results. Adding schema markup can make your site more visible and bring in more visitors.
On-page SEO parts are key to improving your website. Fixing things like title tags and meta descriptions helps search engines understand your site. This boosts your rankings and makes your site easier for people to use.
Here’s how it helps:
More visitors, as better rankings bring more clicks.
Better brand recognition, making your business stand out.
Builds trust, as optimized sites seem more reliable.
Start improving your on-page SEO now to make your site easier to find, trusted, and enjoyable to use.
FAQ
What is the difference between on-page and off-page SEO?
On-page SEO improves parts of your website, like titles and keywords. Off-page SEO works outside your site, such as getting backlinks or using social media. Both help your site get noticed online.
What are keywords, and why are they important?
Keywords are words people type into search engines to find things. They tell search engines what your page is about. Using the right keywords helps your site show up in searches.
What tools can help with on-page SEO?
Tools like Google Search Console, Yoast SEO, and SEMrush are useful. They check your site, suggest better keywords, and fix things like tags and URLs.
What is schema markup, and how does it work?
Schema markup is special code added to your site. It helps search engines show extra details, like ratings or event times. This makes your page stand out and gets more clicks.
What happens if you don’t optimize on-page SEO elements?
Without fixing on-page SEO, search engines may not understand your site. This can lower your rankings and bring fewer visitors. Optimizing helps your site perform better in searches.
